
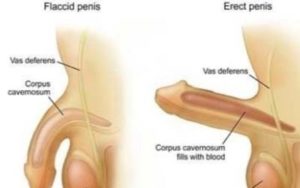
1 What is ED?
Erectile dysfunction, also known as ED is the inability to attain or sustain an erection satisfactory for sexual penetration. ED can also mean a lack of excitement, pleasure and desire for sex. In plain English, if a man cannot get his penis up or keep it up for intercourse or he feels indifferent to sex, he might suffer from ED.
2 Can ED be a normal occurrence? Is it treatable? What is characterised as ED?
An occasional inability to maintain an erection is considered normal and happens to most men. However, if a man is unable to gain and maintain an erection more than fifty percent of the time or for three months or longer, it indicates underlying problems and it is highly likely that he needs treatment. Approximately four percent of men in their fifties and seventeen percent of men in their sixties experience ED. The incidence drastically increases to forty seven percent of men seventy-five and older. Although the incidence of ED increases with age, ageing does not directly cause ED. As people get older, they tend to have more injuries and develop other conditions or diseases that affect the blood flow to the penis. Being healthy and sexually active, a man can have orgasm into 80; therefore, at any age having erectile dysfunction is not normal and it is very important to note that ED is treatable at all ages.
3 What are the causes of ED?
There are many possible causes of ED. Causes can be psychological or physical in nature, or both factors can be at play. Therapists now believe the causes of ED are ninety percent physical and ten percent psychological in nature. There are two types of ED: organic, primary or physical ED and functional, secondary or psychological ED. When exploring the possible physical causes of ED, whether it is disease, injury, or the use of medications which is identified– in many cases, it is the adverse effect on the blood flow to the penis that impedes the initial erection or interrupts the existing erection prematurely.
Possible Primary or Physical causes of ED
- Diseases
- Diabetes: It is estimated that between 35 and 50 percent of men with diabetes suffer from ED
- Vascular Disease: atherosclerosis of the penile arteries and inadequate impedance of venous outflow, also termed venous leakage
- Peyronie’s Disease: accumulation of scar tissue in the shaft of the penis which is likely caused by inflamed blood vessels. It is common in men aged 40 to 60 and most frequent in men who suffer from arthritis and other related diseases.
- Other diseases that have been linked to ED are kidney disease, alcoholism, heart disease, hypertension, and obesity.
- Neurologic Causes: People suffer from some kind of damage to or loss of functions of nerves around or near the penis.
-
- Prostate surgery: This procedure has a forty percent incidence of erectile dysfunction
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord injuries
- Stroke
- Hormonal Causes:
- Cushing’s syndrome: caused by prolonged exposure of the body’s tissues to high levels of the hormone cortisol. It is relatively rare and most commonly affects adults aged 20 to 50. People who are obese and have type 2 diabetes, along with poorly controlled blood glucose—also called blood sugar—and high blood pressure, have an increased risk of developing the disorder.” ED is a symptom of Cushing’s syndrome
- Hypogonadism: This disease affects men with significantly low testosterone levels and is associated with reduced libido. Hypogonadism may contribute slightly to ED both physically and psychologically (lack of desire for sex), but studies suggest that increasing the testosterone levels does not always correct the ED.
- Other possible hormonal causes of ED are hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), hypothyroidism (under active thyroid), and elevated prolactin levels.
Possible Secondary or Psychological Causes of ED:
- Guilt (infidelity, homosexuality, masturbation etc.)
- Depression
- Fear of intimacy
- Severe anxiety including sexual performance anxiety
- Stress
- Mood disorders
- Inhibited sexual desire
- Low self-esteem
- Poor body image
- Fatigue
- Negative feelings toward partner
- Concern related to penis size
- Lack of sexual desire or drive
- Preoccupation
- Fear of being perceived as undesirable or disgusting by partner
4 What are the treatments for ED? What are the advantages and disadvantages of these?
A list of questions that may be asked by the therapist to develop a clearer picture of the client’s health as it relates to the erectile dysfunction. Treatments include non-surgical interventions such as mechanical and pharmacologic interventions and surgical interventions such as penile implants. Pharmacologic interventions require a referral to a physician or nurse practitioner for implementation and include both oral and injection therapies. Mechanical interventions can be suggested by the sex therapist or sex educator.
|
What it is |
How it works |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Cock ring (Mechanical) |
Is used to maintain an erection. Is worn around the penis or around the penis and the scrotum. Used together with VED. |
Low cost, easy to apply, easy to purchase, no need a prescription |
Might pull or pinch the pubic hair If worn for extended periods of time, it might cause nerve damage. Ejaculation might be impeded |
|
VED (Vacuum Erection Device (Mechanical) |
Erections last up to 30 minutes. The pump is used to create negative air pressure surrounding the penis. This pressure causes an increase in blood flow through the vessels of the penis. |
Works for almost everyone. Quick way to achieve and erection. Relatively economical ($300-500) |
Lack of ease when use for the first few times. Penises might be discoloured, cold to touch or numb. Temporary, painless occasional bruises on the shaft of the penis. |
|
Oral medications (Pharmacologic ) |
Viagra, Levitra, Cialis (PD5 inhibitor). These drugs increase the effectiveness of nitric oxide, a chemical that relaxes the muscle in the penis, to allow an increase in blood flow. |
Regardless the cause of ED, these work most of the time. Cialis is safe for daily use. |
Need prescription. Need assistance of sexual stimuli to get hard. Common side effects are headaches, runny nose and diarrhoea. Not recommended for people with diabetes, vascular diseases. |
|
Penile suppositories or injections (Pharmacologic) |
Drugs contain a hormone called Prostaglandin. Brand names include Caverject, Edex, Papaverine, Invicorp, Regitine, Alprostadil. The drugs cause the muscle tissue in the penis to relax and widen the blood vessels. |
Produce an erection quickly without the need for sexual stimulation. |
Need a prescription. Possible side effects include scarring of the penis, prolonged erection and pain at the site of injection. For urethral route, more side effects are recorded such as dizziness, lightheadedness and burning sensation in the urethra. |
What can Sheila’s Approach Massage training and Nuru do for people with ED? A combination of these massages and training sessions are designed to help men get in touch with their body, connect their mind and their body better, and explore their senses further. It is hoped that these practices can bring people excitement and increase blood flow to their penis and therefore improve their ED condition or get rid of it altogether. They are especially helpful with people whose causes of ED are psychological or hormonal. Also, in order to have a healthy and strong erection, a change in lifestyle is a must. It is recommended that men should quit smoking, reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption, exercise regularly, eat a healthy balanced diet, reduce stress, maintain a healthy weight, limit sugar consumption, and get regular medical check ups.
